Telnet is a standard protocol with STD number 8. Its status is recommended. It is described in RFC 854 – Telnet Protocol Specifications and RFC 855 – Telnet Option Specifications. The term is sometimes said to be a shortened form of "terminal network."
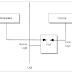
The Telnet protocol provides a standardized interface, through which a program on one host (the Telnet client) can access the resources of another host (the Telnet server) as though the client were a local terminal connected to the server. See Fig. 6.1 for more details. For example, a user on a workstation on a LAN can connect to a host attached to the LAN as though the workstation were a terminal attached directly to the host. Of course, Telnet can be used across WANs as well as LANs.Most Telnet implementations do not provide you with graphics capabilities.
Telnet provides users with a bidirectional interactive text-oriented communication system utilizing a virtual terminal connection over 8-bytes. User data is interspersed in-band with Telnet control information over the TCP (transmission control protocol). Often, Telnet is usually used on a terminal to execute functions remotely.
The user connects to the server by using the Telnet protocol, which means entering Telnet into a command prompt by following this syntax: telnet hostname port. The user then executes commands on the server by using specific Telnet commands into the Telnet prompt. To end a session and log off, the user ends a Telnet command with Telnet.
Explain the working of Telnet.
 Reviewed by enakta13
on
October 03, 2012
Rating:
Reviewed by enakta13
on
October 03, 2012
Rating:
 Reviewed by enakta13
on
October 03, 2012
Rating:
Reviewed by enakta13
on
October 03, 2012
Rating:
